Contents
- The establishment of the ICVCM and Core Carbon Principles
- Building market confidence around carbon credits
- ICROA: a leading voice in the guidance of the ICVCM
- The voluntary carbon market as a key component of a sustainable future
Share this article
Carbon offsetting, carbon credits, and the voluntary carbon market have recently been the subject of much scrutiny and discussion. The examination of certain carbon offsetting projects and carbon standards has given rise to questions around the methodologies and benchmarks being used across the market – which, in turn, has led to discussions around their value, and to what extent the voluntary carbon market is regulated.
The voluntary carbon market allows organisations and individuals responsible for carbon emissions to take voluntary climate action by contributing to certified carbon removal and avoidance projects, and operates as a self-regulated market. It does, however, make use of rules and practices from the regulated market, which sets a limit on the number of tonnes of carbon dioxide that can be produced by organisations which pollute heavily.
As a result, the voluntary carbon market is built around similar standards, methodologies, and independent verification as the regulated market, and is continuously developed to align with new scientific insights and developments.
Currently, 50% of European emissions are regulated – and companies which account for the other, unregulated 50% use the voluntary carbon market to manage their residual emissions.
The establishment of the ICVCM and Core Carbon Principles
In an effort to set and enforce clear global standards, and improve the quality and governance of the voluntary carbon market, the Integrity Council for the Voluntary Carbon Market (also known as the ICVCM or the Integrity Council) was founded in early 2021.
The ICVCM encompasses deep and varied expertise from across the voluntary carbon market ecosystem, with representation from across key stakeholder groups including experts in carbon market technologies, sustainable finance, NGOs, UNFCCC process expertise, regulatory affairs, the corporate sector, science and academia, local communities, and indigenous people.
The ICVCM recently published its Core Carbon Principles (CCPs), a global benchmark for high-quality carbon credits that set rigorous thresholds around disclosure and sustainable development, to improve the integrity and transparency of the voluntary carbon market. Developed with input from hundreds of organisations from across the voluntary carbon market, including Anthesis, the CCPs are an important step towards improved clarity and trust across the market, and highlight the importance of communicating clearly and accurately about offsetting projects.
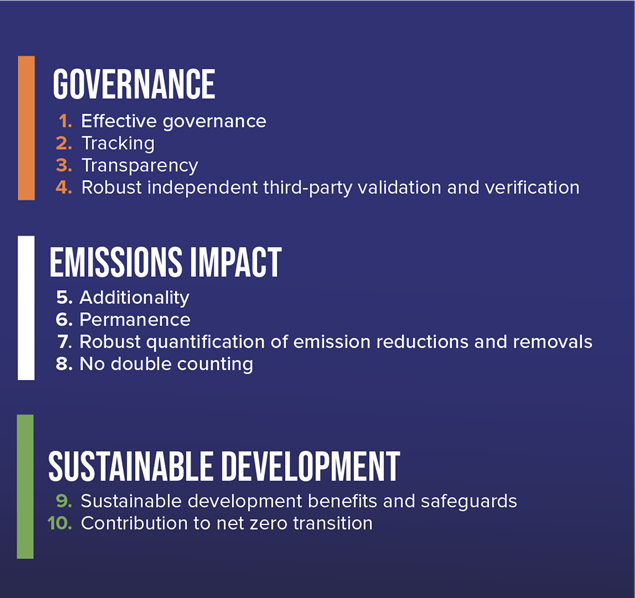
Building market confidence around carbon credits
The CCPs address how each project calculates and quantifies its emissions impact and how social and environmental co-benefits are assessed – details which are essential for building market confidence around carbon credits. Eligible voluntary carbon market projects, which include all Corsia standards (i.e., Gold Standard, Verified Carbon Standard, CDM, ACR, and CAR), will be assigned a CCP label.
This CCP label focuses on three main themes: Governance, Emissions Impact and Sustainable Development, and can include the following attributes:
- Paris Agreement Article 6 approval, if a host country is making use of this option,
- An adaptation fund contribution of 2%, and
- Sustainable Development Goals (only if quantified).
The CCP framework, which will be updated every three years, has significant potential to establish a positive standard for integrity within the carbon market, and is set to add value and garner support. The first CCP-eligible projects and approved categories will be announced later this year.
ICROA: a leading voice in the guidance of the ICVCM
Another organisation which played a key role in setting the guidelines for the ICVCM is the International Carbon Reduction and Offsetting Alliance (ICROA). ICROA has been a leading voice in the voluntary carbon market for over a decade, providing quality assurance and guidance on emissions reductions and high-quality offsetting.
ICROA provides a framework for responsible corporate climate action through the use of carbon credits, the quality of carbon credit supply, and delivering impact to increase ambition. In their Code of Best Practice, ICROA aims to define international best practice for offset-inclusive carbon management and represents the minimum requirements which all ICROA accredited organisations must meet.
The voluntary carbon market as a key component of a sustainable future
As a member and founding partner of ICROA, Anthesis fully supports a transparent and ethical voluntary carbon market as a fundamental step towards a sustainable future. We fully adhere to ICROA’s Code of Best Practice around carbon footprint reduction and offsetting – both of which are important parts of a holistic Net Zero strategy. Our ICROA membership ensures our climate compensation projects are of the highest quality and meet internationally recognised standards. We also offer our own quality assessment, which includes additionality as a key criterion, while following a strict due diligence process before purchasing any credits.
Anthesis will continue to follow the developments within the ICVCM closely, and will contribute to and support efforts to make the voluntary carbon market more transparent, viable and accessible for all. Emissions reduction alone is not enough to meet the targets laid out in the Paris Agreement; only by working on avoidance, reduction and offsetting in parallel can we truly take full responsibility for our impact now.

